Abstract
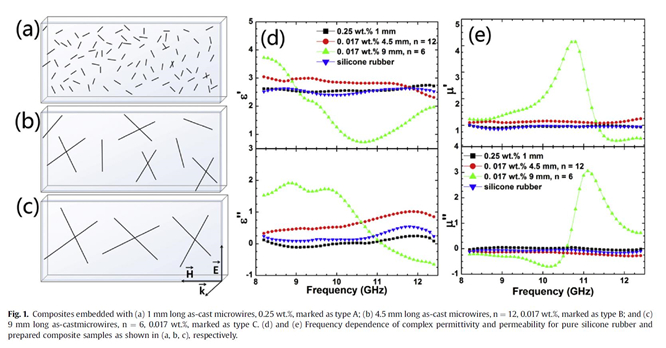
A set of composite absorberswith ultra-low loading of down to 0.017 wt.% short-cut microwires were preparedand investigated in terms of their magnetic and micro-wave properties in theX-band (8–12 GHz). The key parameters that could factor into the performance ofthe present absorbers have been systematically studied from micro to macroscale, i.e., the magnetic domain structure modulated by different internalstress scenarios, microwire aspect and composite filling ratio, and relativeimportance of impedance matching and materials loss. Longer wires (9 mm) andwires after suitable treatment lead to the enhancement of microwave absorbingproperty mainly due to the larger magnetic loss resulted from the naturalferromagnetic resonance, which is induced in the domain rotation and reversalprocess. The internal stress modification by removal of glass and jouleannealing has profound effects in formulating the microwave absorptionfrequency and intensity of microwires composites by tailoring the domain structureand local anisotropy field. It is found that the composites with microwiresannealed at 132 mA for 15 min obtain the minimum reflection loss and broadestabsorption bandwidth with reference to -10 dB at 1.5 mm thickness, which is-25.7 dB (0.81 GHz) at 11.39 GHz caused by the relative high attenuationconstant and best matching condition where Zreal is 1.026 and Zimag is -0.102.This indicates that impedance matching plays a dominant role in tailoring themicrowave absorbing property. Remarkably, the unconventional absorptionfrequency - matching thickness relation violating the quarter-wavelength modeloffers possibility to address the limitation of thickness for low frequencyabsorbing application.
Zheng X F, Qin FX, Wang H, et al. Microwave absorbing properties of composites containingultra-low loading of optimized microwires[J]. Composites Science &Technology, 2017, 151.